Pore size
1D, 2D and 3D pore size
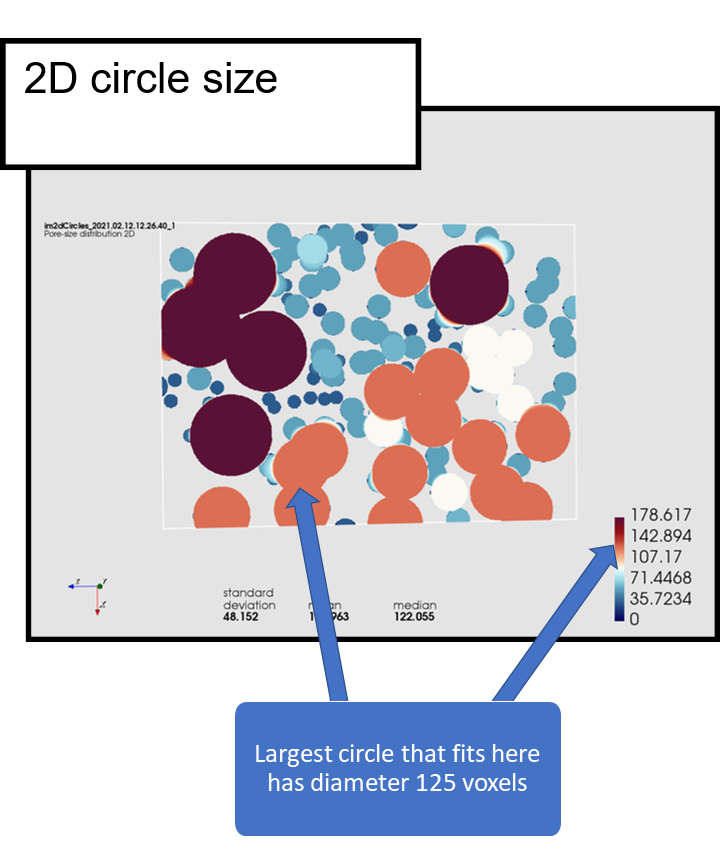
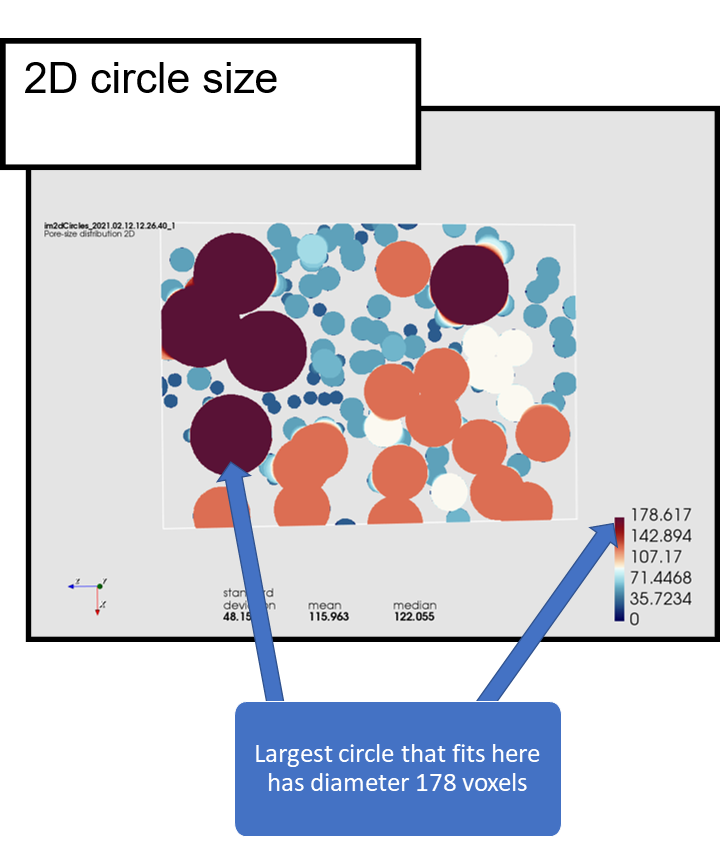
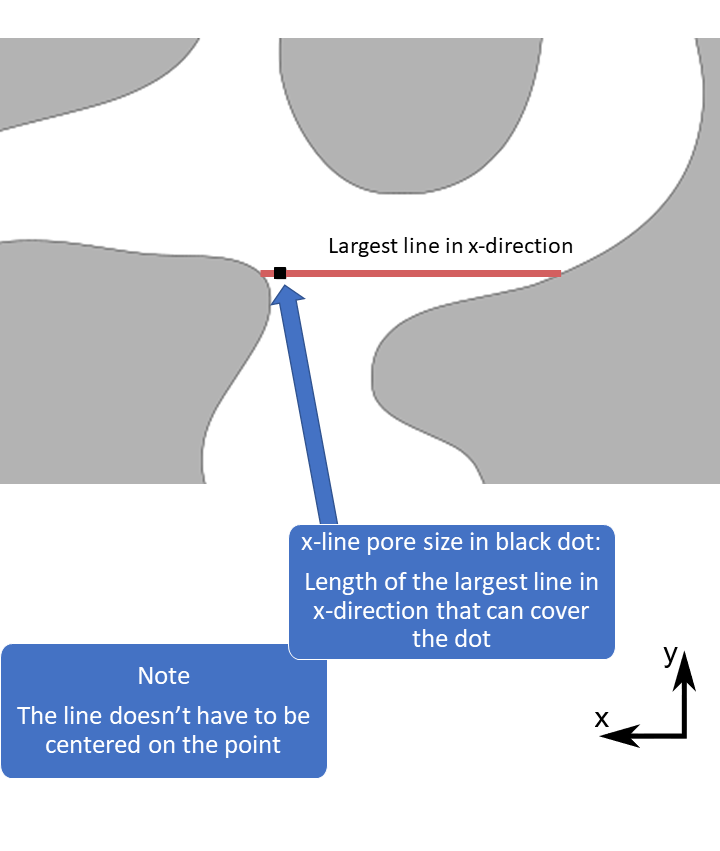
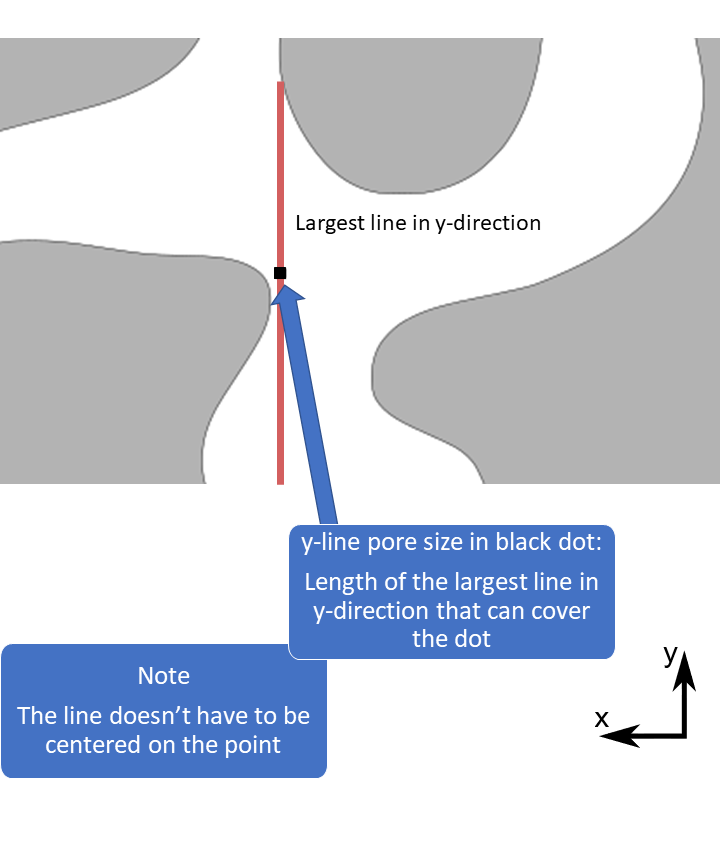
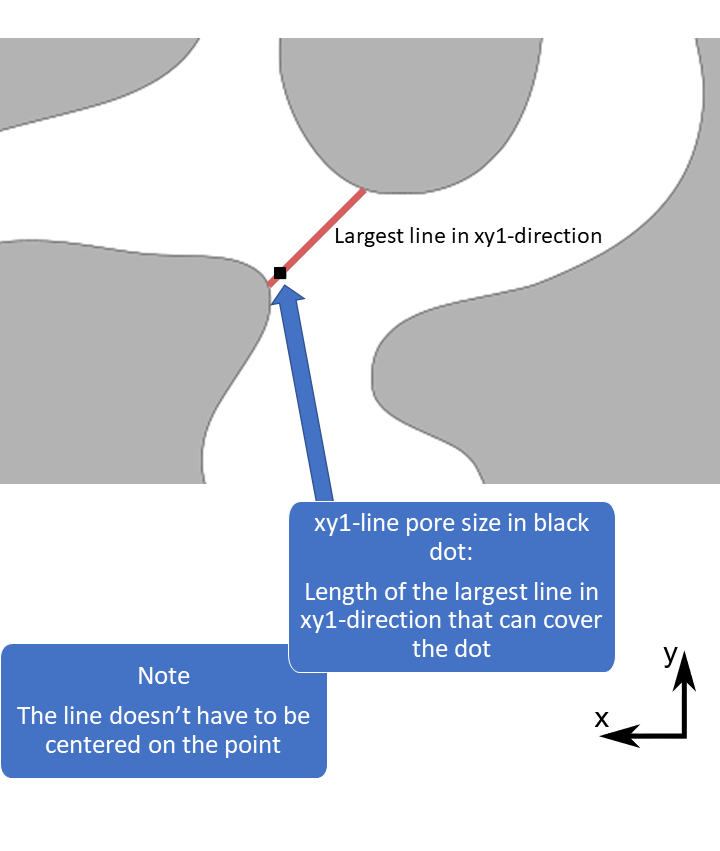
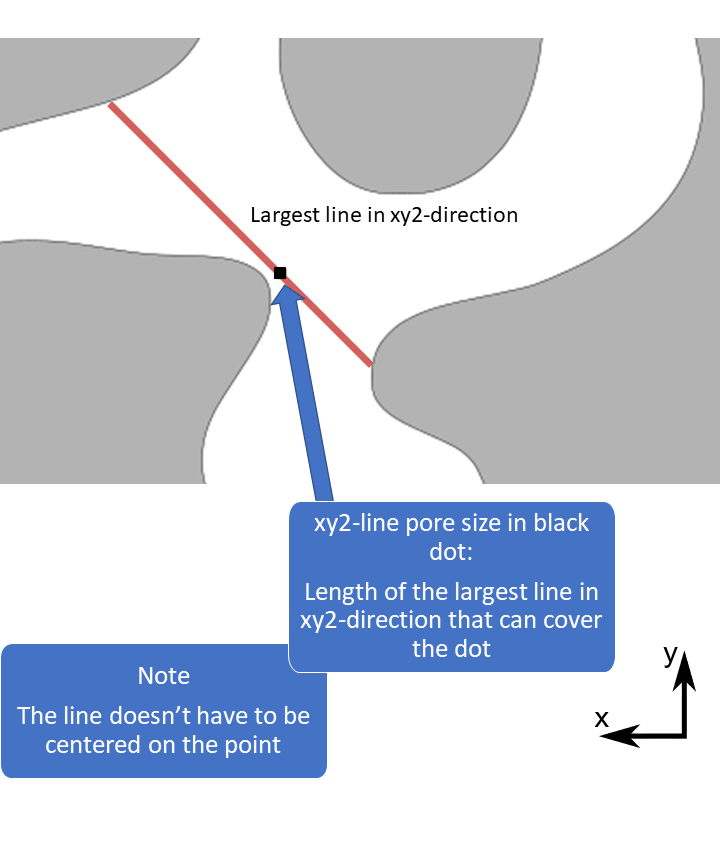
The pore size methods are useful for quantifying the size and shape of irregularly shaped objects. This kind of pore size is measured with respect to simple objects, such as spheres, circles and lines (called structuring elements). The pore size in a point is defined as the size of the largest object, for example the diameter of the largest sphere, that can fit in the pore space and cover the point.
In Mist, you can fit
•Spheres (3D pore size)
•Circles (2D pore size)
•Lines (1D pore size)
The 3D pore size is also called granulometry, aperture map and maximum inscribed spheres.
In Mist
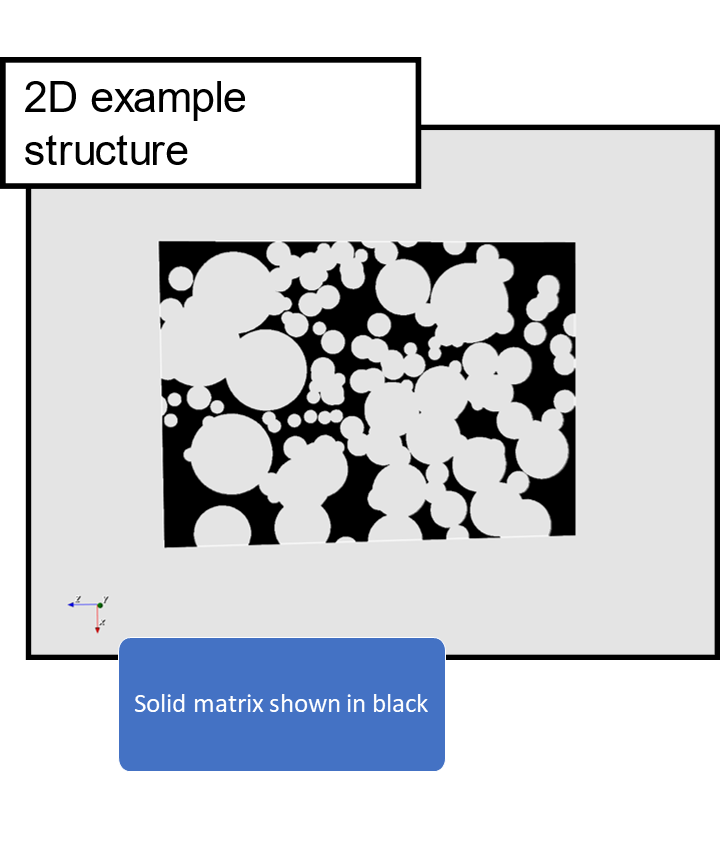
Each pore voxel in the 3D output is assigned the value of the pore size (or max pore size, see below). Solid matrix have value 0.
The implementation of the pore size methods in Mist is described in detail in the reference manual (see also Scientific resources).
2D pore size illustration
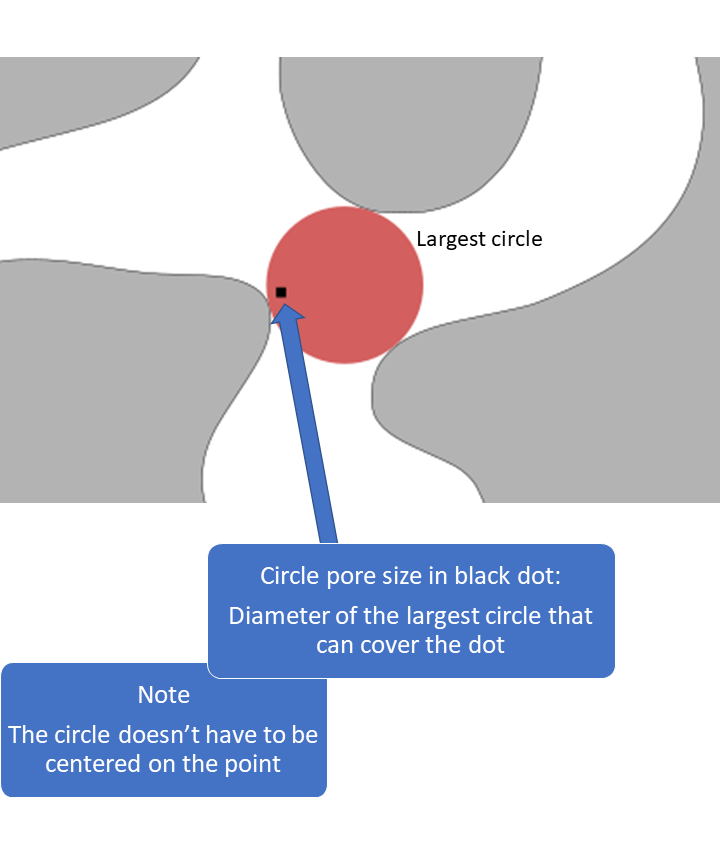
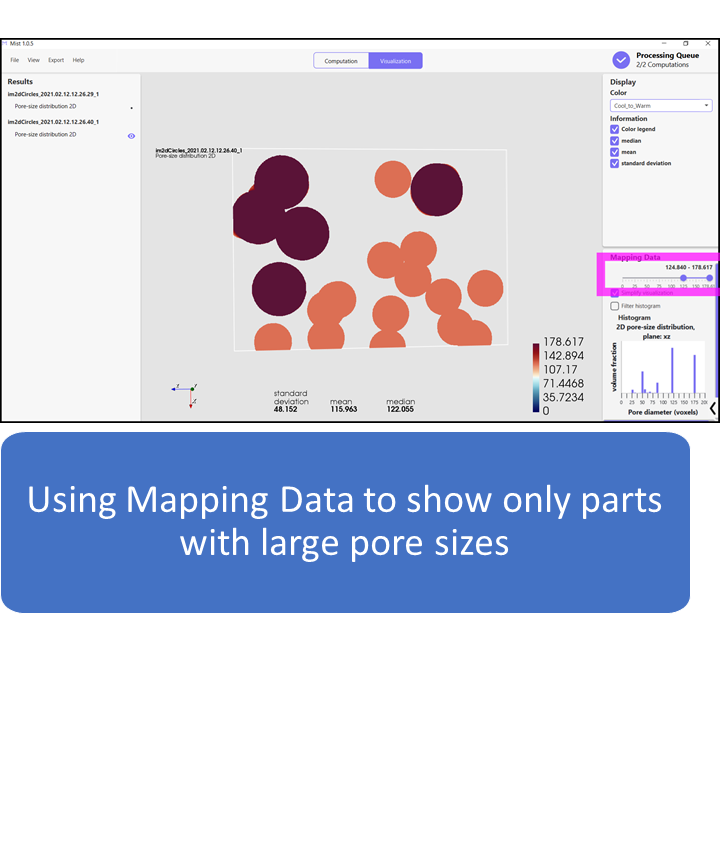
2D pore size in Mist
Anisotropy measured by max size/max direction
Measure shape and directionality/anisotropy in Mist by computing pore sizes with respect to lines or circles.
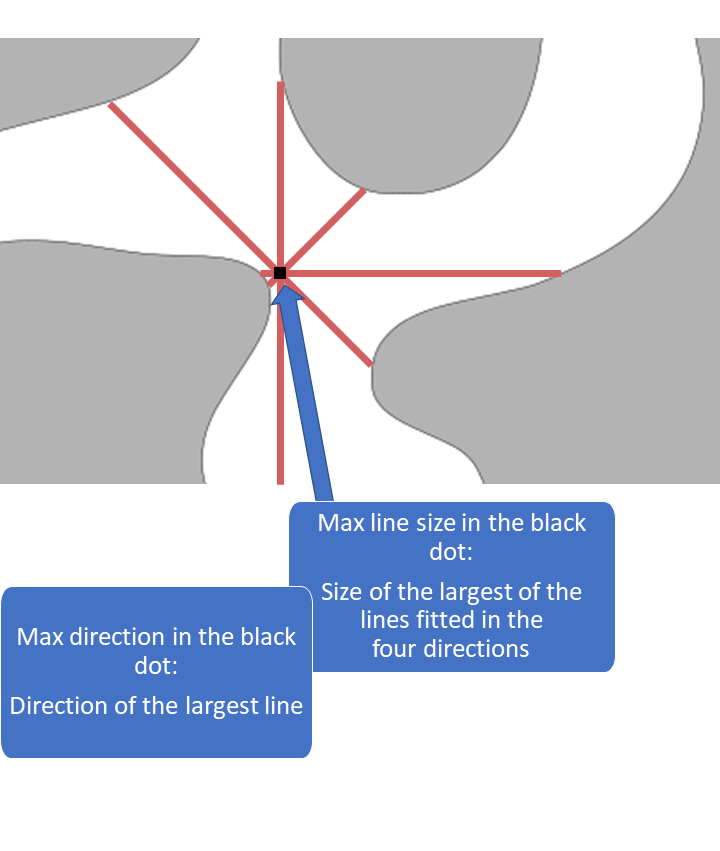
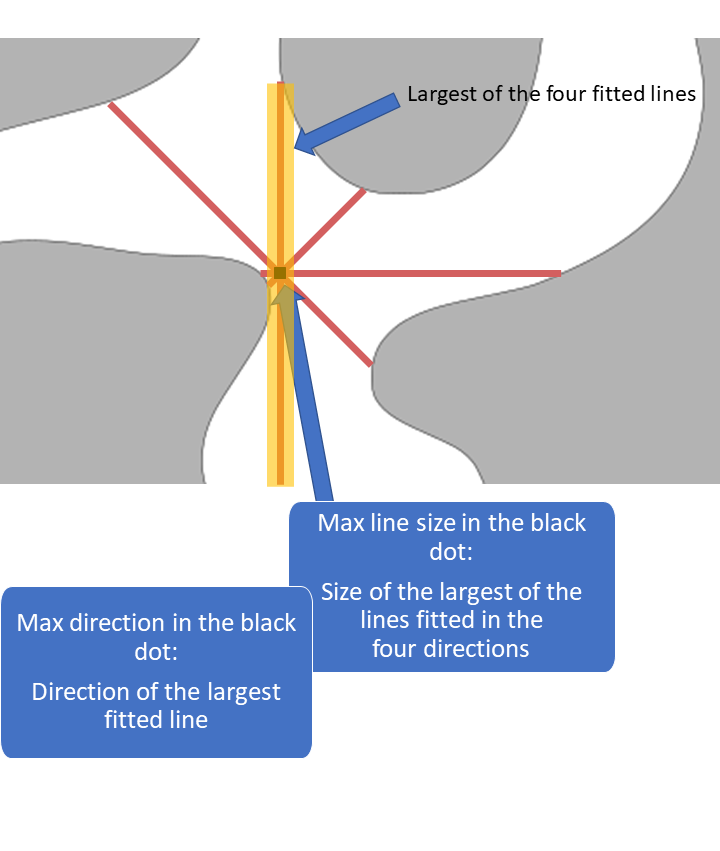
Definition, local max size
The local max size in a point p is the maximum local line (circle) pore size in p out of all the computed line (circle) sizes.
Definition, local max direction
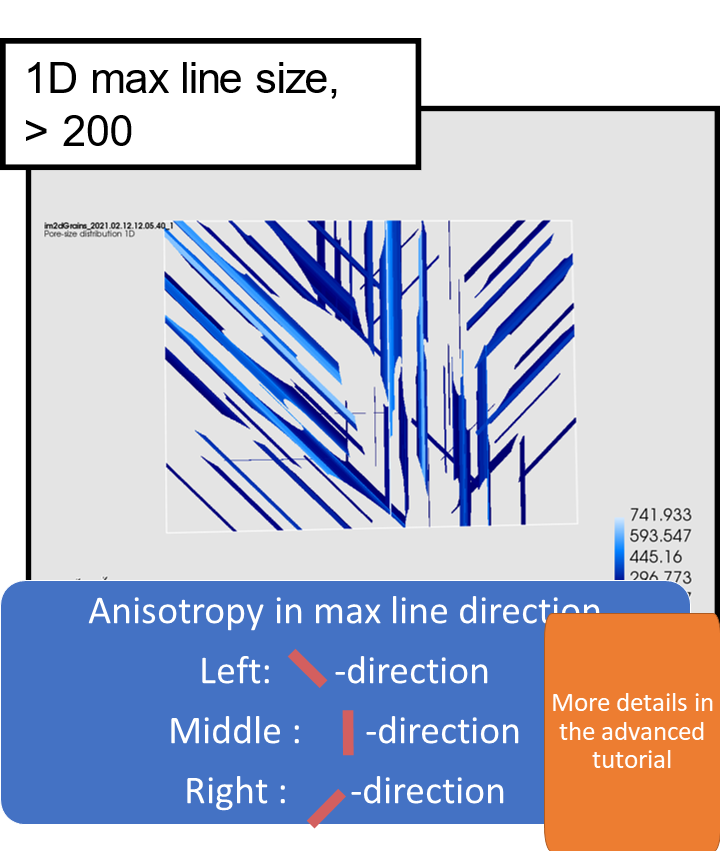
The local max direction (orientation) in a point p is the direction (orientation) that has the largest local line (circle) size.
In Mist
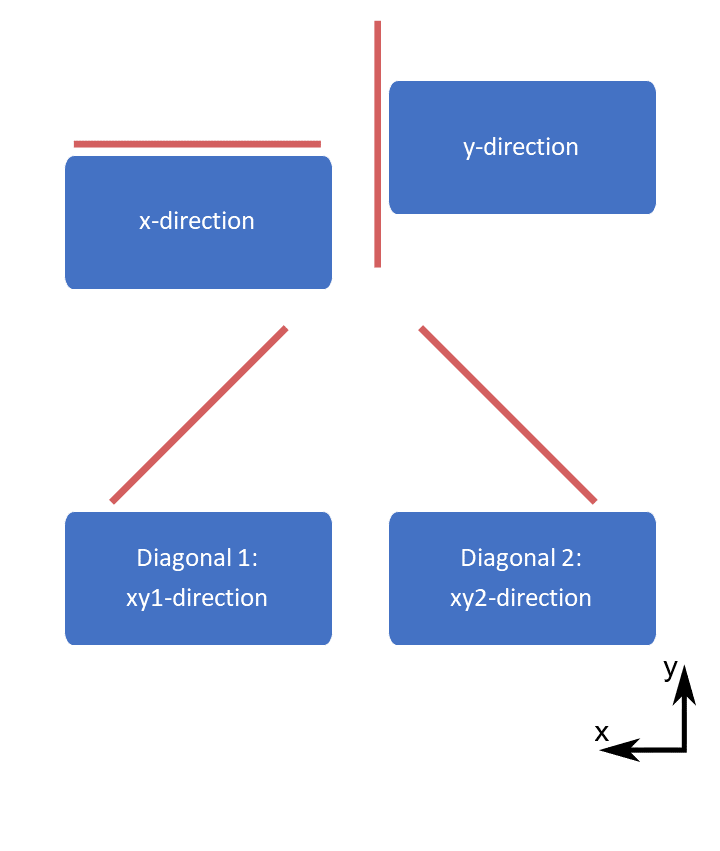
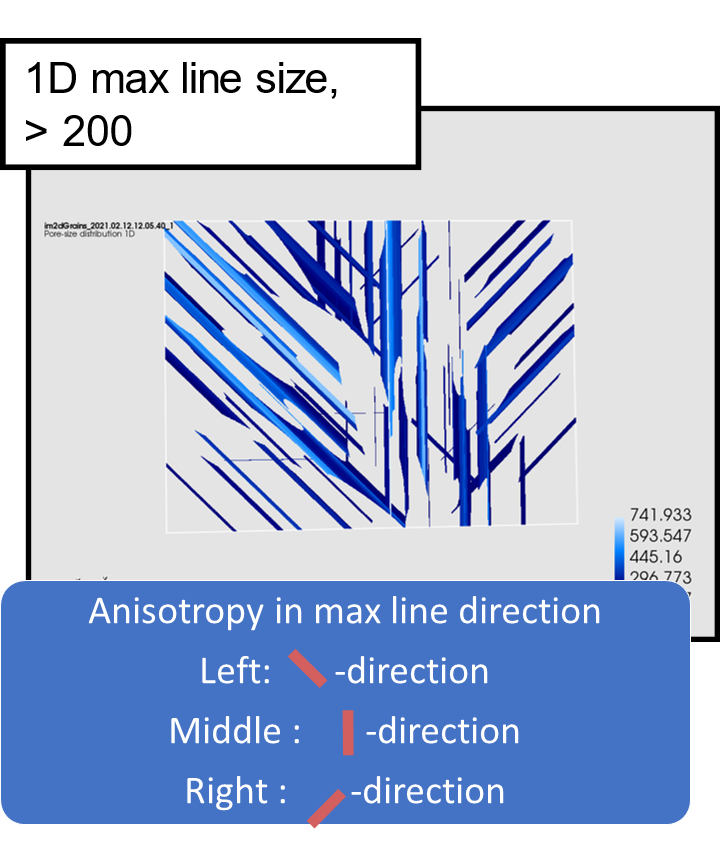
1D pore sizes: lines are computed in 13 different directions and circles in 3 orientations. The 13 directions are the x-, y-, and z-direction, diagonals in the xy-, xz- and yz-planes, and diagonals crossing the unit cube. Only the max size and max direction are returned. Note: it is recommended to use the solid boundary condition for 1D pore sizes, see the reference manual for details.
2D pore sizes: The orientations for circles are the xy-, xz- and yz-planes. Choose between computing pore sizes for circles oriented in one of the three directions, or computing the max size over all three directions.
Measure pore shape by comparing the max line size, max circle size and sphere size.
Measure anisotropy by the distribution of max directions. Note: currently only histograms of max size are visible in Mist. To show histograms of 1D max direction in Matlab, open the output vtk-file in Paraview or use this supplied Matlab code for post-processing of vtk-files as shown in this video (shown for geodesic distance-output). The Matlab code automatically loads and prints histograms and related data for all vtk-files created in Mist in a specified folder.
1D pore size illustration,
max size and max direction
1D pore size in Mist
The video below shows how to compute the 3D pore size and the 1D pore size in Mist for a demo structure that can be downloaded from here. See also this video from Tutorial, Part I which shows 3D and 1D pore size computed in a more complex structure.