Getting started with the GUI
Computing geometry characteristics
See the videos in Tutorial, Part II and Tutorial, Advanced use for instructions on how to compute each geometry characterization method.
You can load and run computations on several geometry-files at the same time. Note that the same computation settings are applied to all loaded geometry files, whereas file settings are set individually for each file. The computation and file settings are described in detail in the reference manual.
Input
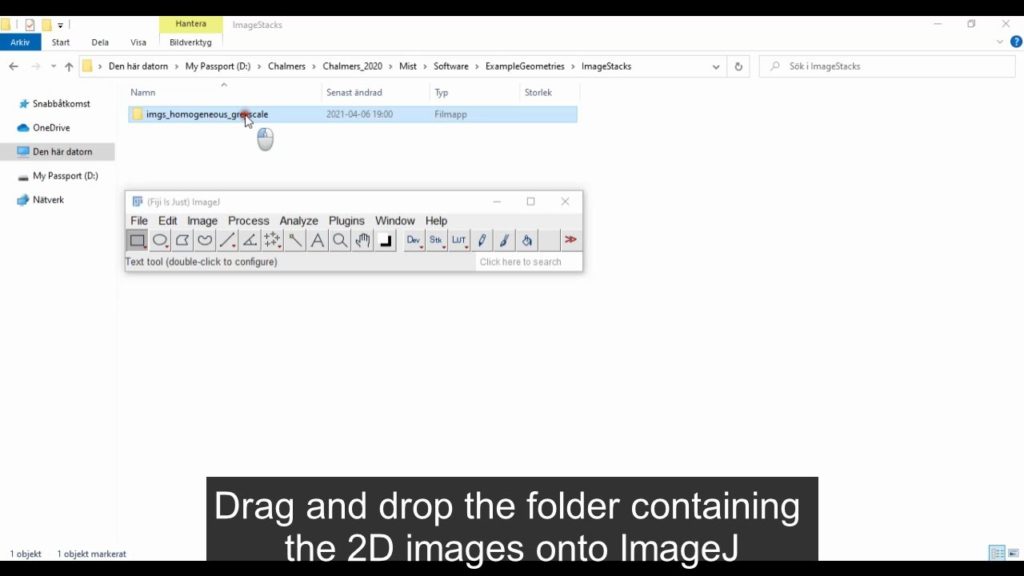
The geometry characterization methods in Mist require 3D input files (geometry files). Accepted file-types are 3D tif-stacks and 3D vtk-files. You can create 3D tif-stacks from 2D images in many image processing software, see the video below for instructions on how to do that using the free software ImageJ.
To get started, download demo structures that are used in the tutorial videos from here.
The geometry characterization methods require binarized/segmented structures. If you load a grey-scale image, you can segment it in Mist using a fixed threshold as shown in the video. You can also use the computation method Binarize which includes more sophisticated binarization methods.
Input files
Output
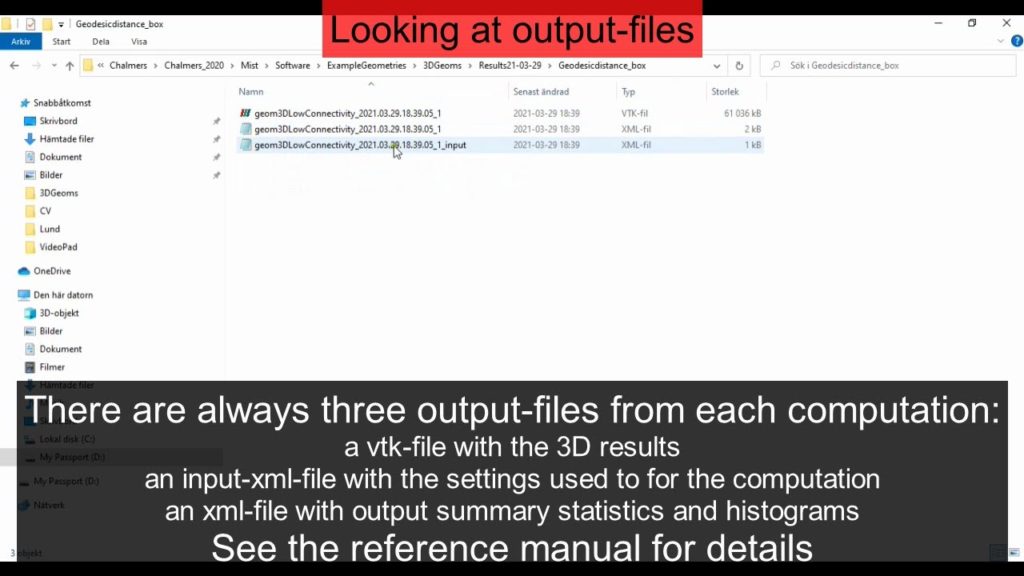
Output files
Each computation results in three output files which are saved to the result-folder as shown in the video below: an input-xml-file with the computation settings, an xml-file with histograms and summary statistics such as mean values and standard deviations, and a vtk-file with 3D results. See the reference manual for details about the output from each geometry characterization method.
Exporting images
Export images of the 3D visualizations and histograms as shown in the video below.
Re-loading previous results
Save the current state as a project to re-load the results at a later time, as in the video below.